High-silica zeolite Y is a desired catalytic material for oil refining and thepetrochemical industry,which consumption ranks the first in the solid catalysts.However, the physique of Al-rich framework of zeolite Y brings a fatal drawback in hydrothermal stability toward its practical applications. To alleviate this issue, dealumination processes have been employed in order to achieve the high silica counterparts.It is worth mentioning thatthe loss of crystallinity and mass as well as the creation of defects and dealumination gradient seems always inevitable for post-treatment process.
Hence, the direct crystallization is the ideal rout to the synthsis of high silica Y.For the past decades enormous efforts have been made to improve SAR ofzeolite Y.However, its direct synthesis remains a symbolicchallenge inmodern zeolite science, with a limited improvement of theframework SiO2/Al2O3ratio (SAR) from ~5 to 9.
Recently a research group led by Prof. Tian Peng and Prof. Prof. Liu Zhongmin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a new strategy to directly synthesize high silica zeolite Y with SAR as high as 15.6. The results were published in Adv. Mater.
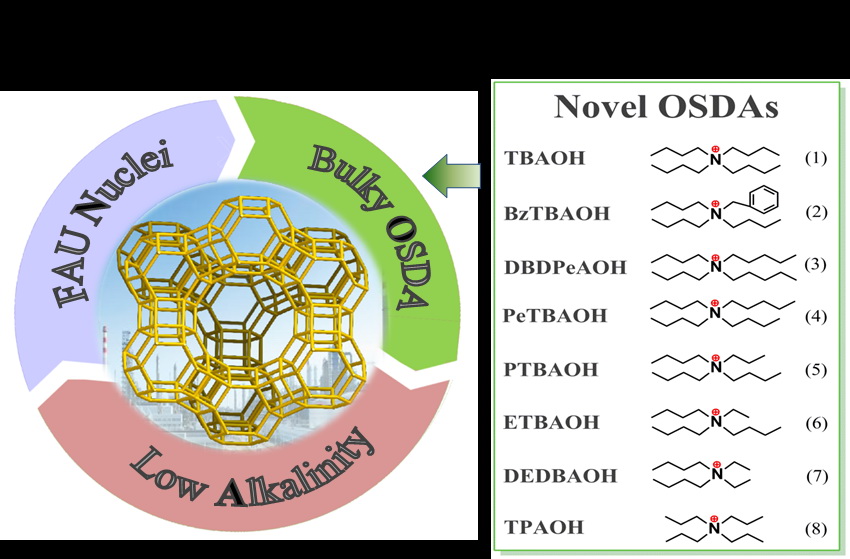
NOA-co strategy and novel OSDAs for the synthesis of high silica zeolites Y
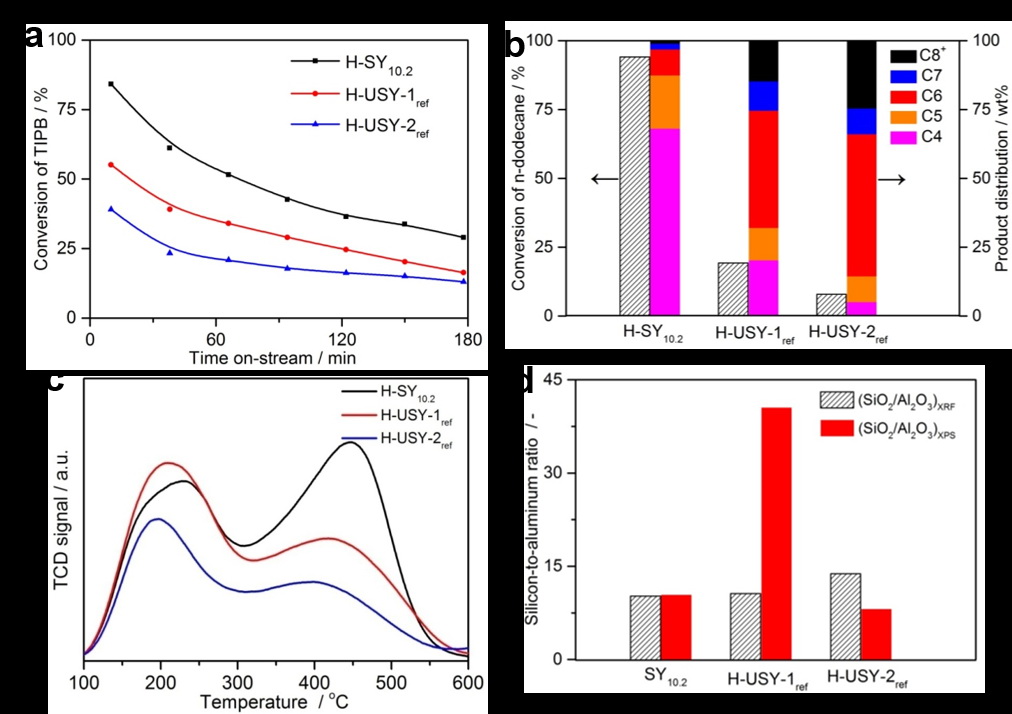
Catalytic cracking performance, acidity and Al distribution of high silica zeolite Y
The novel strategy, named NOA-co strategy, involved the use of highly dispersed FAUnuclei solution, bulkyorganicstructure directing agent (OSDA) and lowalkalinity synthetic gel.A series of quaternary alkylammoniumions is discovered as effective OSDAs based on the NOA-co strategy, and therelevant crystallization mechanism is elucidated. Moreover, the high-silicaproducts are demonstrated to have greatly improved (hydro)thermal stability,high concentration of strong acid sites, and uniform acid distribution, whichlead to superior catalytic performance in the cracking of bulky hydrocarbons.It is anticipated that this synthetic strategy will benefit thesynthesis anddevelopment of zeolitic catalysts in a wide range of reaction processes.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21676262,21991091), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (QYZDB-SSW-JSC040,QYZDY-SSW-JSC024), and DICP Funding (DICPZZBS201807). (Text and image by Zhu Dali and Wang Lin ying)
A Bottom-Up Strategy for the Synthesis of Highly Siliceous Faujasite-Type Zeolite. Dali Zhu, Linying Wang, Dong Fan, Nana Yan, Shengjun Huang, Shutao Xu, Peng Guo, Miao Yang, Jianmin Zhang, Peng Tian*, Zhongmin Liu*, Advanced Materials, 32(26):2000272, 2020.