Researchers reported new progress in aromatization mechanism of coupling reaction of light alkanes with CO over acidic zeolites
Author: Time:2021-10-12 Click:
Aromatics production mainly comes from naphtha catalytic reforming, but it is difficult to produce aromatics from light naphtha (mainly C4-C6 alkanes). At present, zeolites modified by metal Ga and Zn are mainly used as catalysts for the aromatization of light alkanes, which are prone to irreversible deactivation such as agglomeration and sintering. Although H-form zeolites have good stability and are widely used in the field of petrochemical industry, catalytic aromatization of light alkanes over these catalysts will produce a large number of small alkanes (methane and ethane), and the selectivity of aromatics is greatly limited.
From the prospective of hydrogen carbon ratio (H / C) of elements, the hydrogen carbon ratio of aromatic products is lower than that of light alkanes, which means that excess hydrogen needs to be removed during the aromatization of light alkanes. Based on this, we consider introducing hydrogen deficient substances such as CO during the conversion of low-carbon alkanes. In previous research, DNL1203 research team has found that the introduction of CO in the conversion of n-hexane can change the H / C ratio of the product and obtain high aromatics selectivity (ACS catalyst. 2020, 10, 7, 4171 – 4180). However, the mechanism of the coupling reaction between alkanes and CO is not very clear.
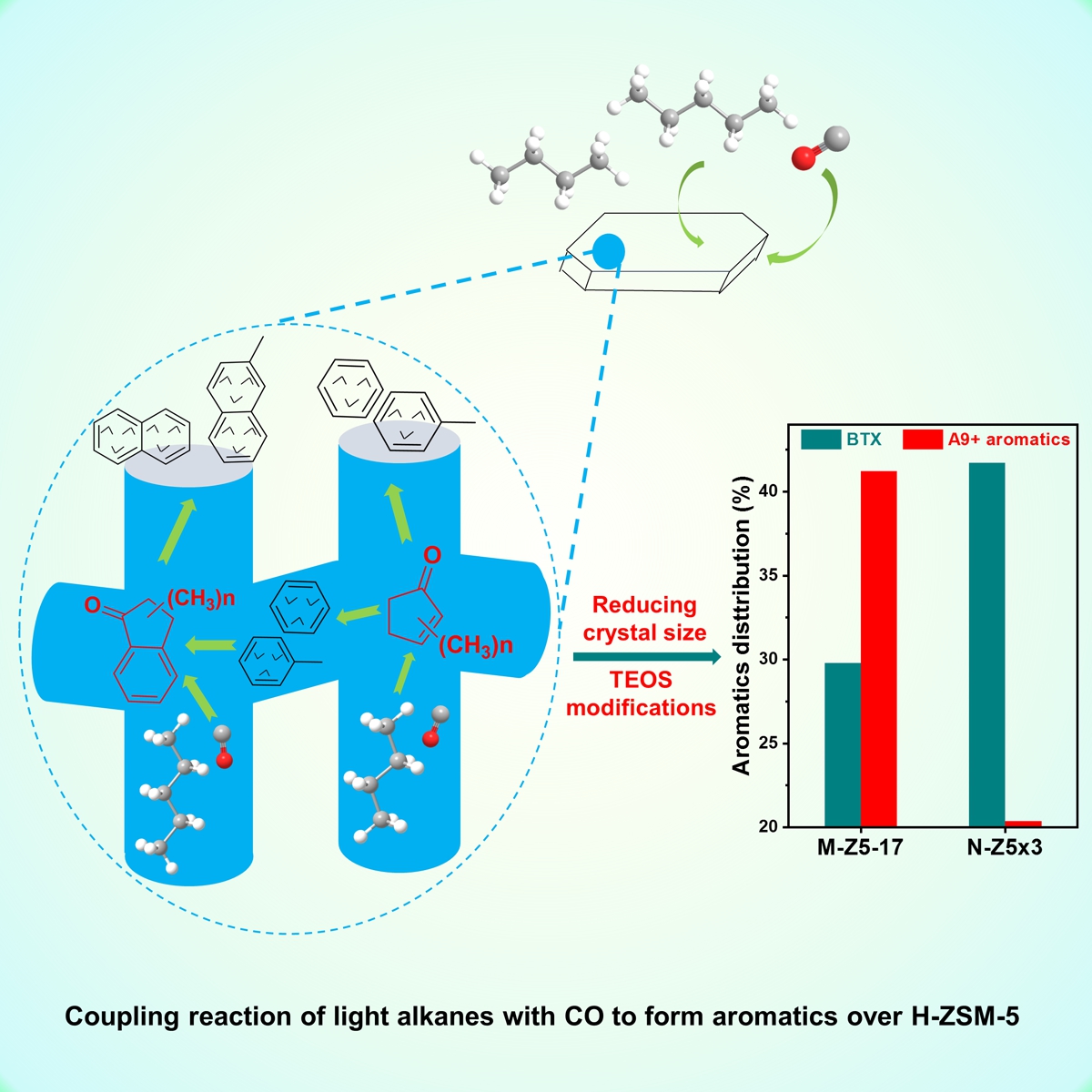
Recently, the research team has made new progress in the coupling mechanism of light alkanes (with carbon less than 6) and Co. It is found that the introduction of CO can significantly improve the selectivity of aromatics in the conversion of light alkanes. During the coupling of cyclopentane and CO over H-ZSM-5, the aromatics selectivity can reach 85%. Important intermediates such as cyclopentenonewere detected and their formation and evolution mechanism were clarified. The complete process of the coupling reaction was successfully revealed by in-situ IR, in-situ UV, solid-state NMR, isotope tracing and molecular sieve carbon deposition: (1) CO inserts into carbenium ions to form acylium cations, (2) acylium cations react with olefins to generate unsaturated ketones, (3) unsaturated ketones cyclize to methyl-substituted cyclopentenones, (4) methyl-substituted cyclopentenones convert to mononuclear aromatics.
This work puts forward a new idea for the conversion of light alkanes and CO, and has industrial application prospects.
Aromatization mechanism of coupling reaction of light alkanes with CO over acidic zeolites: Cyclopentenones as key intermediates, Chem Catalysis (2021), DOI: 10.1016/j.checat.2021.09.004.