The acid properties of SAPO-34 molecular sieves (MSs), includingthe strength and density of Brönsted acids, have attracted enormous attention inpast decades because of the excellent performance of SAPO-34 in industrialprocesses such as the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) process and the selectivecatalytic reduction of NOxwith NH3(NH3-SCR). Currently, pure-phase SAPO-34MSs with different Si contents can be easily obtained by utilizing multifariousorganic structure-directing agents (OSDAs). However, the resulting SAPO-34MSs have different acid properties, which may affect their catalytic performance.Hence, correlating the acid properties with the OSDAs and Si contents is ofsignificance to synthesize SAPO-34 MSs with the desired properties.
In this article, theacid properties of four series of SAPO-34 MSs with varying Si contents synthesized using tetraethylammonium hydroxide(TEAOH),diisopropylamine (DIPA), n-butylamine (nBA), and morpholine (MOR) as the OSDAswere probed in detail bythermogravimetry (TG), Rietveld refinement, and solid-statenuclear magnetic resonance (ss-NMR) analyses.
This work was published in Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin. on May18.
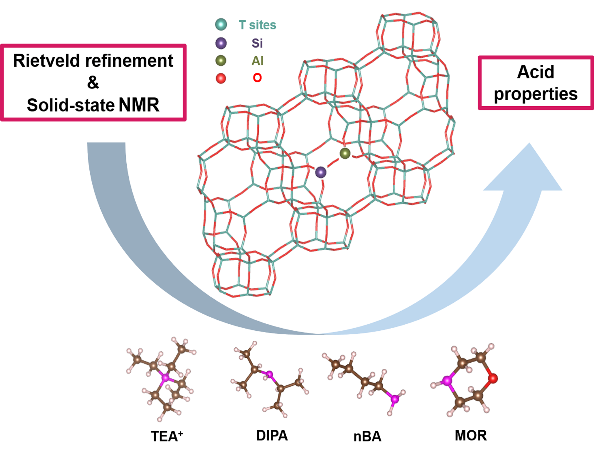
The acid properties of SAPO-34 are systematically probed with the assistant of Rietveld refinement and solid-state NMR.
The results of TG and Rietveld refinement showed that the SAPO-34 MSstemplated by TEAOH and DIPA have only one OSDA percha(one of the composite building units) cage in the longitudinalconfiguration, while those templated by nBA and MOR possess two OSDAs occluded in thechacage in an up-and-downarrangement.Interestingly, the acid strength of SAPO-34 templated by TEAOH increased with increasing Si content, whilethe acid density remained almost unchanged. In contrast, the acid density of SAPO-34 templated by DIPA decreasedevidently with an increase in the Si content, while the acid strength showed only a small variation. Among the other twosamples, SAPO-34 templated by MOR has the most amounts of acid densities compared to SAPO-34 templated by nBA,while the strength is not superior. Thus, we conclude that the acid density is associated with the number of OSDAs in eachchacage and their protonation ability, while the difference in acid strength is attributed to the number of Si atoms at theedges of the Si islands. The findings of this study will provide insight into the acid properties of related crystalline porousmaterials.
This work was supported bythe National Natural Science Foundation of China, the CAS Pioneer Hundred Talents Program, the Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, (DNL) Cooperation Fund, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the KeyResearch Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Acid Properties of SAPO-34 Molecular Sieves with Different Si Contents Templated by Various Organic Structure-Directing Agents. Lei Wang, Tantan Sun, Nana Yan, Xiaona Liu, Chao Ma, Shutao Xu, Peng Guo*,Peng Tian, Zhongmin Liu*, CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS, 37:2003046, 2021.